

The beginning of life on Earth and its evolution over billions of years continue to intrigue researchers worldwide. The central dogma or the directional flow of genetic information from a deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) template to a ribose nucleic acid (RNA) transcript, and finally into a functional protein, is fundamental to cellular structure and functions. DNA functions as the blueprint of the cell and carries genetic information required for the synthesis of functional proteins. Conversely, proteins are required for the synthesis of DNA. Therefore, whether DNA emerged first or protein, continues to remain a matter of debate.
This molecular version of the “chicken and egg” question led to the proposition of an “RNA World.” RNAs in the form of ‘ribozymes’ or RNA enzymes carry genetic information similar to DNA and also possess catalytic functions like proteins. The discovery of ribozymes further fueled the RNA World hypothesis where RNA served dual functions of “genetic information storage” and “catalysis,” facilitating primitive life activities solely by RNA. While modern ribosomes are a complex of RNAs and proteins, ribozymes during early evolutionary stages may have been pieced together through the assembly of individual functional RNA units.
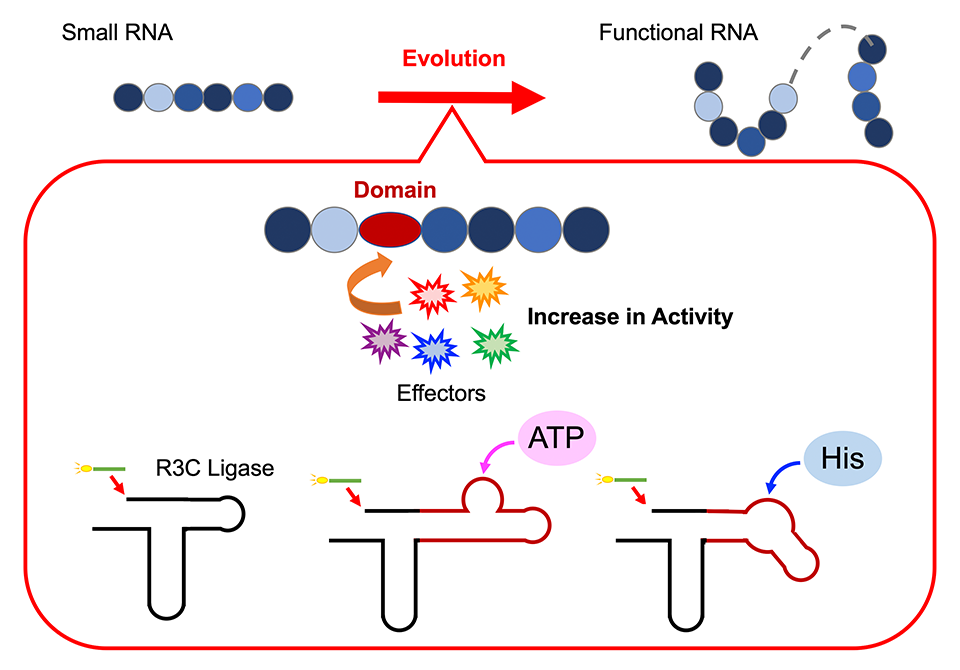
To test this hypothesis, Professor Koji Tamura, along with his team of researchers at the Department of Biological Science and Technology, Tokyo University of Science, conducted a series of experiments to decode the assembly of functional ribozymes. For this, they designed an artificial ribozyme, R3C ligase, to investigate how individual RNA units come together to form a functional structure. Giving further insight into their work published on 17 April 2024, in Life, Prof. Tamura states, “The R3C ligase is a ribozyme that catalyzes the formation of a 3’,5’-phosphodiester linkage between two RNA molecules. We modified the structure by adding specific domains that can interact with various effectors.”

Within ribosomes, which are the site of protein synthesis, RNA units assemble to function as Peptidyl Transferase Center (PTC) in a way such that they form a scaffold for the recruitment of amino acids (individual components of a peptide/protein) attached to tRNAs (featured in Nature magazine (https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-00574-4)). This is an important insight into the evolutionary history of protein synthesis systems, but it is not sufficient to trace the evolutionary pathway based on the RNA World hypothesis.
To explore if the elongation of RNA, achieved by linking individual RNA units together, is regulated allosterically, the researchers altered the structure of the R3C ligase. They did this by incorporating short RNA sequences that bind adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a vital energy carrier molecule in cells, into the ribozyme. The team noted that R3C ligase activity was dependent on the concentration of ATP, with higher activity observed at higher concentrations of ATP. Further, an increase in the melting temperature (Tm value) indicated that the binding of ATP to R3C ligase stabilized the structure, which likely influenced its ligase activity.
Similarly, on fusing an L-histidine-binding RNA sequence to the ribozyme, they noted an increase in ligase activity at increasing concentrations of histidine (a key amino acid). Notably, the increase in activity was specific to increasing concentrations of ATP or histidine; no changes were observed in response to other nucleotide triphosphates or amino acids. These findings suggest that ATP and histidine act as effector molecules that trigger structural conformational changes in the ribozyme, which further influence enzyme stability and activity.
ATP is the central energy carrier of the cell which supports numerous molecular processes, while, histidine is the most common amino acid found in the active site of enzymes, and maintains their acid-base chemistry. Given, the important roles of ATP and histidine in RNA interactions and molecular functions, these results provide novel insights into the role of RNA in early evolution, including the origin of the genetic code. Furthermore, engineered ribozymes such as the one developed in this study hold significant promise in a myriad of applications including targeted drug delivery, therapeutics, nano-biosensors, enzyme engineering, and synthesis of novel enzymes with uses in various industrial processes.
Overall, this study can offer insights into how the transition from the RNA World to the modern “DNA/Protein World” occurred. A fundamental understanding of the RNA World in turn, can enhance their use in real-life applications.
“This study will lead to the elucidation of the process of ‘allostericity-based acquisition of function and cooperativity’ in RNA evolution. The RNA-RNA interactions, RNA-amino acid interactions, and allostericity applied in this research can guide the fabrication of arbitrary RNA nanostructures, with various applications,” concludes Prof. Tamura.

