
A team of researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center has developed a nanotechnology platform that can change the way the immune system sees solid tumor cells, making them more receptive to immunotherapy. The preclinical findings suggest this adaptable immune conversion approach has the potential for broad application across many cancer types.
The study, published today in Nature Nanotechnology, details the use of this platform to artificially attach an activation molecule to the surface of tumor cells, triggering an immune response in both in vivo and in vitro models. Wen Jiang, M.D., Ph.D., assistant professor of Radiation Oncology, and Betty Kim, M.D., Ph.D., professor of Neurosurgery, co-led the study.
“With this new platform, we now have a strategy to convert a solid tumor, at least immunologically, to resemble a hematological tumor, which often has a much higher response rate to immunotherapy treatments,” Jiang said. “If we are able to translate and validate this approach in the clinic, it may enable us to get closer to the maximum level of activity from immunotherapy drugs with cancers that have not traditionally responded well.”
Immunotherapy has high response rates in blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, but success has been variable across solid tumors. Scientists have been working to further understand the mechanisms prohibiting a better response. One explanation is that varied expression of immune regulatory molecules on blood cancer versus solid tumor cells impact how they interact with immune cells.
The signaling lymphocytic activation molecule family member 7 (SLAMF7) receptor is critical in activating the body’s immune cells against cancer cells, acting as an “eat me” signal. However, it is found almost exclusively on the surface of blood cancer cells and not in solid tumor cells, making it an attractive target for the researchers’ immune conversion approach.
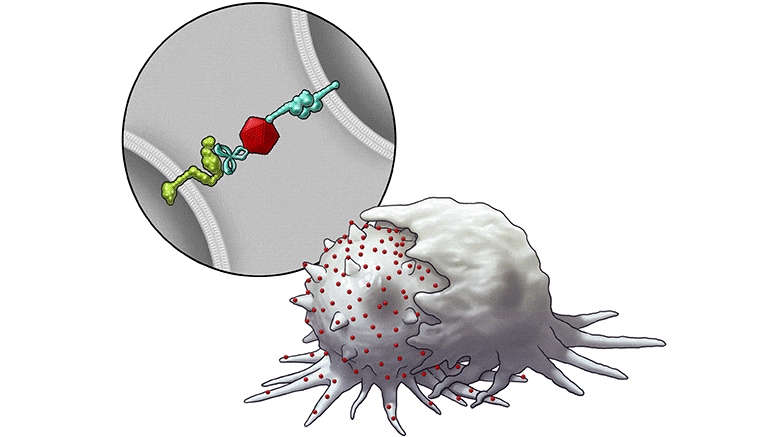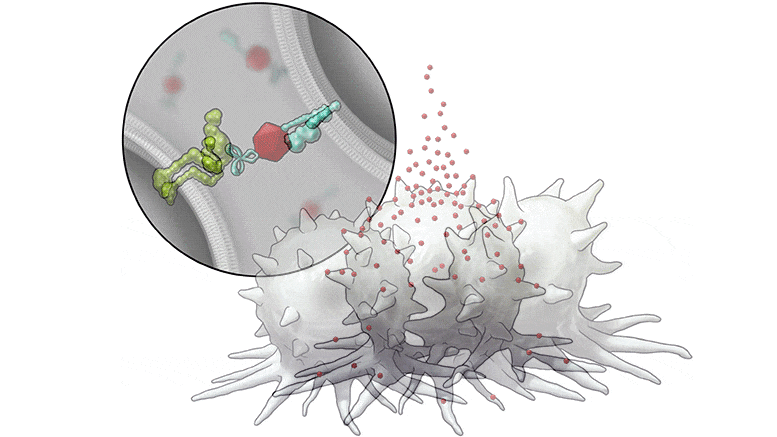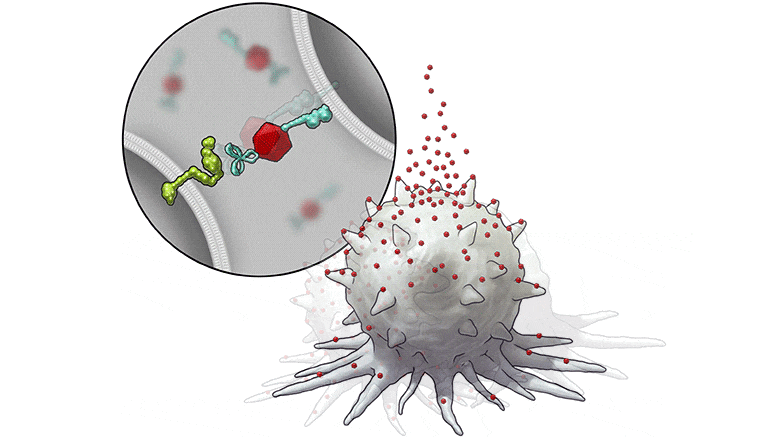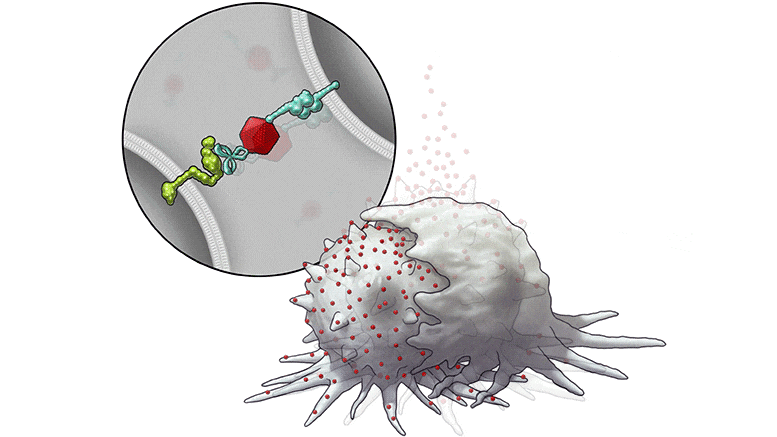
To promote the expression of SLAMF7 on solid tumor cells, the researchers developed their bispecific tumor-transforming nanoconjugate (BiTN) platform. These nanosystems are designed with one molecule to bind to the surface of targeted tumor cells and a second molecule to activate an immune response.
In this study, the researchers used BiTN with SLAMF7 and a HER2-recognizing antibody to target HER2-positive breast cancer cells. In laboratory models, the nanoconjugate successfully attached SLAMF7 to the breast cancer cells, resulting in phagocytosis, or ingestion, by immune cells. The approach also sensitized the breast cancer cells to treatment with an anti-CD47 antibody, which blocks the “don’t eat me” signal from tumor cells to further increase responses in solid tumors.
According to the authors, one of the most exciting things about this platform is its broad potential applications. The approach would not be specific to one cancer type or one regulatory molecule, rather it has the potential to be a universal strategy for several different solid tumor types. As a proof of concept, the authors also developed BiTN with folate instead of the anti-HER2-antibody to target triple-negative breast cancer with similar results.
“Because these are engineered constructs, this can be used as a plug-and-play approach to incorporate different tumor-targeting agents or immune molecules onto the surface of the nanoparticle,” Kim said. “For patients with solid tumors that have not responded to immunotherapy, we see this as an added advantage to target the part of the tumor that didn’t respond.”

